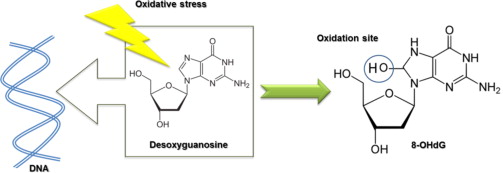
- The menstrual cycle is characterized by repetitive cycles of endometrial proliferation, shedding, and repair. These processes are highly dynamic and involve increased cellular activity, which can lead to DNA damage. Among the various biomarkers for DNA damage, 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) is widely recognized for its specificity and reliability.
- 8-OHdG is a product of guanine oxidation in DNA and is released during repair mechanisms. It can be detected in biological samples such as urine, serum, or tissues, making it a valuable tool for studying DNA damage in menstrual health.
Measurement of 8-OHdG
The 8-OHdG ELISA Kit is a standard method used to detect and quantify 8-OHdG levels in biological samples. It provides accurate and reliable measurements to study DNA damage associated with menstruation.
Key Features of the ELISA Kit :
- Sample Types : Applicable to urine, serum, plasma, or tissue extracts.
- Sensitivity : Detects low concentrations of 8-OHdG, essential for early-stage studies.
- Protocol : Uses a competitive binding assay where sample 8-OHdG competes with a labeled standard for antibody binding, followed by signal quantification.
Applications in Menstrual Health
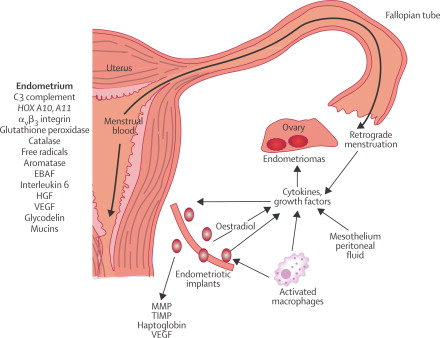
Endometriosis Studies :
- Elevated 8-OHdG levels have been observed in both tissue and urine samples of patients with endometriosis, indicating significant DNA damage.
Evaluating Menstrual Disorders :
- In cases of heavy menstrual bleeding or painful periods, measuring 8-OHdG helps assess the extent of DNA damage in endometrial cells.
Hormonal Therapy Monitoring :
- 8-OHdG levels can be tracked to evaluate the effects of hormonal treatments on reducing DNA damage during the menstrual cycle.
Fertility Research :
- Abnormal DNA damage, as indicated by increased 8-OHdG, may impair endometrial receptivity and affect implantation outcomes.